pinia学习篇
pinia
认识Pinia(和vuex对比)
Pinia 是 Vue 的专属的最新 状态管理,是 Vuex 状态管理工具的替代品,pinia更适配vue3
和vuex的区别
1.提供更加简单的API (去掉了mutation)
2.提供符合,Composition组合式风格的API(和 Vue3 新语法统一)
3.去掉了modules的嵌套结构,每一个store都是一个独立的模块,不再是vuex的单一组件树
4.配合TypeScript更加友好,提供可靠的类型推断
5.不再有命名空间的概念,不需要记住它们的复杂关系
Pinia安装和基本使用
npm install pinia
创建js文件,注册导入Pinia
创建store文件夹,在里面创建index.js
1 | import { createPinia } from 'pinia' |
在main.js中挂载pinia实例
1 | import { createApp } from 'vue' |
pinia管理数据
后续希望Pinia管理的数据,在store文件夹创建对应的.js文件,每个想要定义的单独数据单独放在一个store里
在每个单独的store里面定义仓库defineStore()返回的结果是一个函数,一返回的函数统一用useID命名方式,如useCounterdiefineStore(),在里面传入第一个参数作为仓库的表示,
定义store后会自动管理,直接导出即可
1 | import { defineStore } from 'pinia' |
要使用时Home.vue
1 | import useCounter from '@/store/counter' |
使用数据<h2>count:{{counterStore.count}}</h2>
不需要再.state,直接用数据就可以了
Store
认识Store
一个store (如 Pinia)是一个实体,它会持有为绑定到你组件树的状态和业务逻辑,有点像始终存在,并且每个人都可以读取和写入的组件
可以在应用程序中定义任意数量的store来管理你的状态
Store有三个核心概念:state、 getters、 actions;
等同于组件的data、computed、methods;
一旦store被实例化,你就可以直接在 store 上访问 state、getters 和 actions 中定义的任何属性
定义Store
使用defineStore()定义,返回的函数统一用useX命名方式,具体前面有写
当定义好后,在浏览器调试工具里面可以看到,如图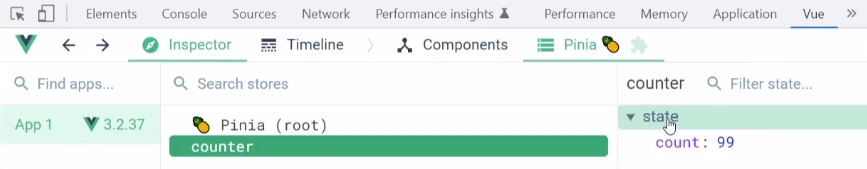
使用数据注意–解构响应性
store不能直接解构,不然会让数据失去响应式:
- 不解构使用数据
1
2
3
4
5import useCounter from '@/store/counter'
const counterStore = useCounter()
function changeCount(){
counterStore.count++ //pinia里面可以直接这样做
}<h2>count:{{counterStore.count}}</h2>,没问题 - 解构错误使用使用解构的数据
1
2
3
4
5
6import useCounter from '@/store/counter'
const counterStore = useCounter()
const {count} = counterStore //这里解构了
function changeCount(){
counterStore.count++ //pinia里面可以直接这样做
}<h2>count:{{count}}</h2>
刚开始能展示出来,但是数据变化count不会跟着变,失去了响应式 - 解构正确使用(toRefs)
如果你非要解构+响应式,使用toRefs使用解构的数据1
2
3
4
5
6
7import useCounter from '@/store/counter'
import { toRefs } from 'vue'
const counterStore = useCounter()
const {count,sum,age} = toRefs(counterStore) //这里解构了
function changeCount(){
counterStore.count++ //pinia里面可以直接这样做
}<h2>count:{{count}}</h2>,现在能成功响应 - 解构正确使用(storeToRefs)
要解构+响应式,也可以用Pinia提供的storeToRefs使用解构的数据1
2
3
4
5
6
7import useCounter from '@/store/counter'
import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'
const counterStore = useCounter()
const {count,sum,age} = storeToRefs(counterStore) //这里解构了
function changeCount(){
counterStore.count++ //pinia里面可以直接这样做
}<h2>count:{{count}}</h2>,现在能成功响应
Pinia核心概念–State
改变State
- 读取和写入 state
默认情况下,可以通过 store 实例访问状态来直接读取和写入状态1
2
3const counterStore =useCounter()
counterStore.counter++
counterStore.name="nienie" - 重置state
$reset()
调用 store 上的 $reset() 方法将状态 重置 到其初始值;
除了直接用store.counter++修改store,还可以调用$patch方法
它允许使用部分state对象同时应用多个更改1
2
3
4
5const counterStore =usecounter()
counterStore.$patch({
counter:100.
name: "nie"
})自己的方法不加
$,如果是他给我们提供的一般有$
Pinia核心概念–Getters
getters相当于store的计算属性,可以在 getters 中定义一个函数,这个函数会返回一个值,这个值会缓存,只有当依赖的 state 发生变化时才会重新计算
getters函数中默认接收一个state作为参数
Getters基本使用
一个getters中也可以引入另外一个getters
1 | import { defineStore } from 'pinia' |
使用:
1 | import useCounter from '@/store/counter' |
<h2>count1:{{counterStore.doubleCount}}</h2><h2>count2:{{counterStore.doubleCountPlusOne}}</h2>
同样不需要写.getters,使用很简洁
getters也支持返回一个函数
1 | import { defineStore } from 'pinia' |
<h2>count2:{{counterStore.getFriendsById(111)}}</h2>返回{id:111,name:"雾刃"}
getters中可以使用别的store中的数据
导入别的store,然后在getters中获取别的store信息,再使用
1 | import { defineStore } from 'pinia' |
Pinia核心概念–Actions
- Actions 相当于组件中的 methods
- 用 defineStore()中的 actions 属性定义,非常适合定义业务逻辑
- 和getters一样,在action中可以通过this访问整个store实例的所有操作
- actions是支持异步操作的,并且可以编写异步函数,在函数中使用await
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
const useCounter = defineStore('storeCounter',{
state:()=>({
count:100,
friends:[
{id:111,name:"雾刃"},
{id:112,name:"枫糖"},
{id:113,name:"松瑰"}
]
}),
getters:{
doubleCount(state){
return state.count * 2
},
// getters中可以引入另外一个getters
doubleCountPlusOne(){
return this.doubleCount + 1
},
getFriendsById(){
return function(id){
for(let i=0;i<state.friends.length;i++){
const item = state.friends[i]
if(item.id === id){
return item
}
}
}
}
},
actions:{
increment(){},
//actions是支持异步操作的
async fetchHomeMultidata(){}
const res=await fetch("http://....")
const data = await res.json()
this.banners = data.data.banner.list
this.recommend = data.data.recommend.list
return data
}
}
)
export default useCounter
Pinia基础使用和持久化工具(旧笔记)
创建项目(按照官方文档安装)
使用 Vite 创建一个空的 Vue3项目
npm ceate vue@latest
这里面的pinia选的No,这里根据官方文档安装pinia,学会后后面直接选Yes
https://pinia.vuejs.org/zh/
这里是vue3使用方法,官方文档也有2的使用方法
首先导包挂载,在项目的main.js中修改代码
1 | import { createApp } from 'vue' |
store
有Option Store和Setup Store,推荐使用后者,模块化,更易维护和操作
在src文件夹中创建store文件夹,在里面创建仓库名.js,每个仓库之间是独立的
1 | import { definestore }from 'pinia' |
action异步实现
pinia的action不需要考虑同步异步,都支持,和组件中获取异步数据的写法完全一致
storeToRefs工具函数
理解:如果直接导入仓库的函数,然后再页面直接结构使用return的数据的值。不进行处理,那么数据会丢失响应式(函数不会,函数可以直接解构)
改进:先导入import {storeToRefs} from ‘pinia’ 然后在结构的时候使用一个方法storeToRefs(函数名)
Pinia持久化插件
官方文档:https://prazdevs.github.io/pinia-plugin-persistedstate/zh/
安装插件 pinia-plugin-persistedstate
官方文档说版本要高于2.0.0,在项目package.json文件夹里的dependencies里面有pinia的版本1
npm i pinia-plugin-persistedstate
在main.js中将插件添加到Pinia实例上
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19//将插件添加到Pinia实例上
//官方文档
import{createPinia}from 'pinia'
import piniaPluginPersistedstate from 'pinia-plugin-persistedstate'
const pinia = createPinia()
pinia.use(piniaPluginPersistedstate)
...
//完整的main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
// 导入持久化的插件
import persist from 'pinia-plugin-persistedstate'
import App from './App.vue'
const pinia = createPinia() // 创建Pinia实例
const app = createApp(App) // 创建根实例
app.use(pinia.use(persist)) // pinia插件的安装配置
app.mount('#app') // 视图的挂载eatePinia().use(persist))配置 store/counter.js
在修改数据的时候优先往本地存,在你刷新的时候优先从本地获取
开启当前模块的持久化:在要配置的.js文件中store的第三个参数添加{
persist: true
}
完成后重启项目,在F12vue中可以看到,也可以在F12的Application中看到存储到本地的数据1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { computed, ref } from 'vue'
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', () => {
...
return {
count,
doubleCount,
increment
}
}, {
persist: true //开启当前模块的持久化
})其他配置看官网文档








